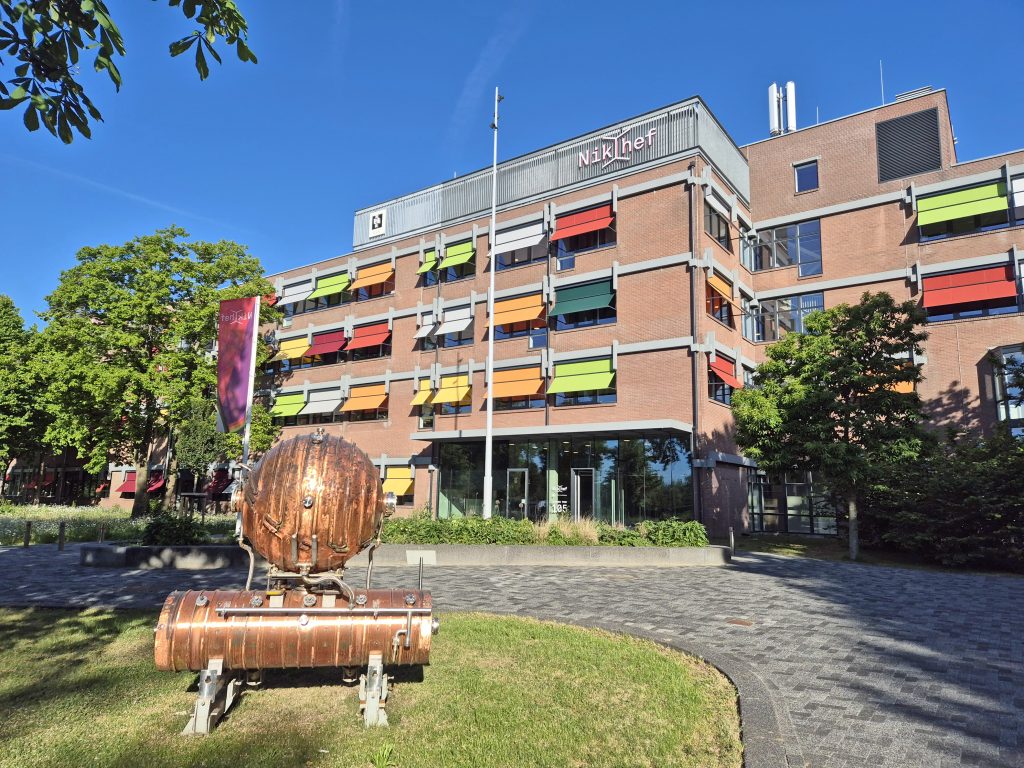
Het Nationaal instituut voor subatomaire fysica Nikhef bestaat dit jaar een halve eeuw. Voortgekomen uit een werkgroep van gelijkgestemde natuurkundigen in de jaren ‘40 is Nikhef nu een landelijk samenwerkingsverband van zes universiteiten en NWO op het gebied van de fysica van deeltjes, kosmische stralen en zwaartekrachtsgolven. Nikhef vormt de thuisbasis voor de Nederlandse inbreng in grote internationale experimenten bij ondermeer CERN in Genève en elders in Europa en de wereld. Scroll omlaag voor de wordingsgeschiedenis van Nikhef en de successen van de afgelopen vijftig jaar.
This year, the National Institute for Subatomic Physics Nikhef celebrates its 50th anniversary. Originating from a working group of like-minded physicists in the 1940s, Nikhef is now a national partnership of six universities and NWO in the field of particle physics, cosmic rays and gravitational waves. Nikhef is the home base for the Dutch participation in major international experiments at CERN in Geneva and elsewhere in Europe and the world. Scroll down for the history of Nikhef and its successes over the past fifty years.
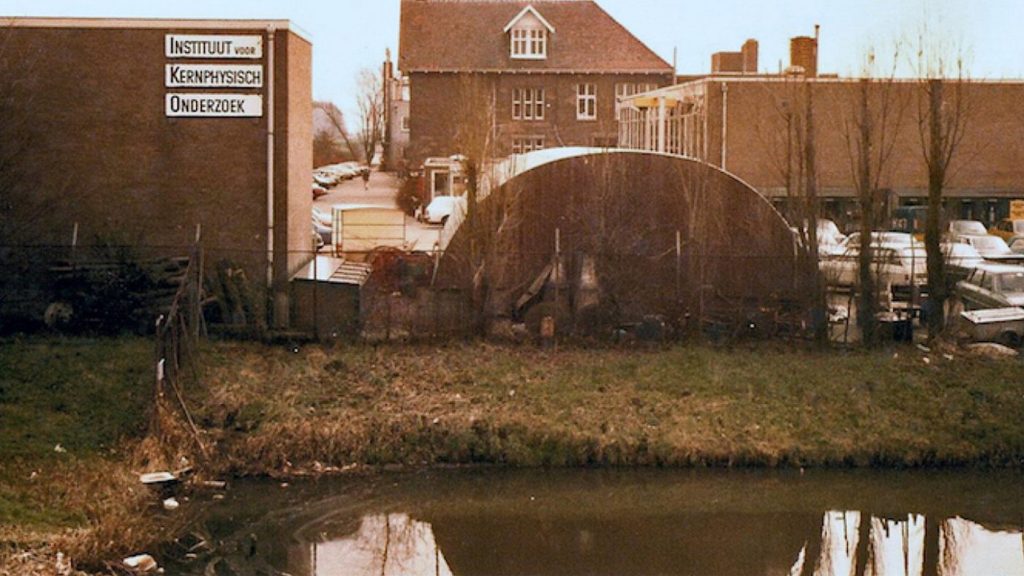
Oprichting van de Stichting FOM voor Fundamenteel Onderzoek der Materie en van het Instituut voor Kernfysisch Onderzoek (IKO) door FOM, Philips en de Gemeente Amsterdam. IKO wordt gevestigd in de Watergraafsmeer in Amsterdam aan de Ooster-Ringdijk.
Establishment of the FOM Foundation for Fundamental Research of Matter and of the Institute for Nuclear Physics Research (IKO) by FOM, Philips and the City of Amsterdam. IKO is based in the Watergraafsmeer in Amsterdam at the Ooster-Ringdijk.
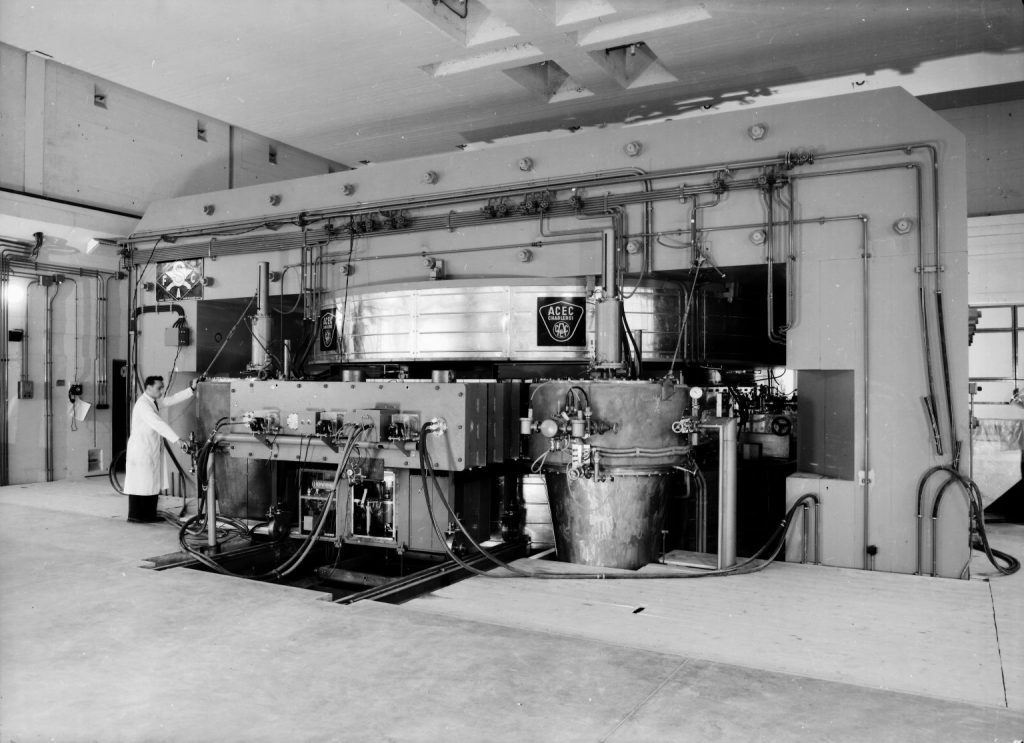
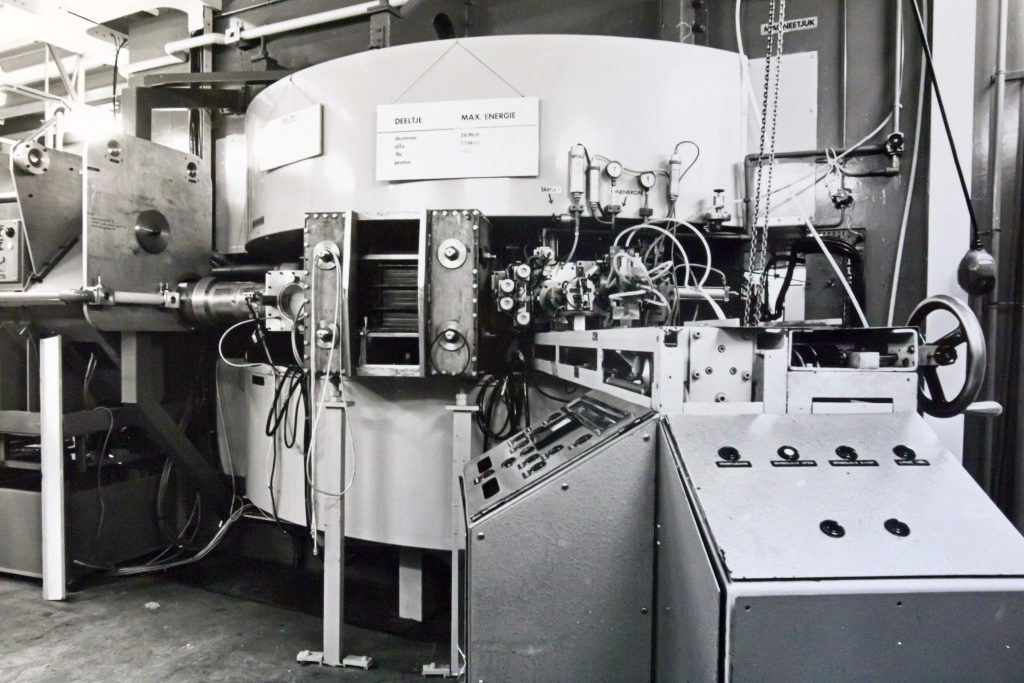
Europa’s eerste synchrocyclotronversneller staat bij IKO in Amsterdam, gebouwd door Philips. Het produceerde bundels van alfadeeltjes en deuterium, later van protonen en helium-3. Experimenten in de kernfysica en productie van radioactieve isotopen voor medische diagnostiek. Gesloten in 1976.
Europe’s first synchrocyclotron accelerator, built by Philips for IKO in Amsterdam. It produced beams of alpha particles and deuterium, later also of protons and helium-3. Experiments in nuclear physics and production of radioactive isotopes for medical diagnostics. Closed in 1976.
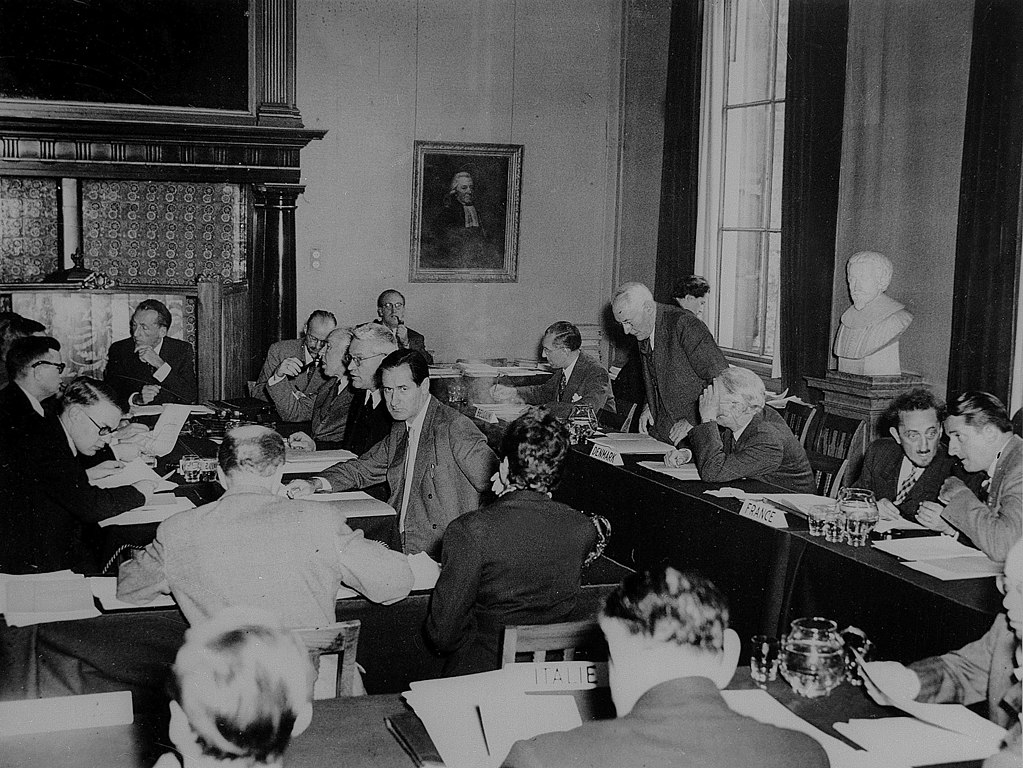
Ondertekening in Amsterdam van het verdrag voor de oprichting van CERN, een laboratorium voor deeltjesonderzoek. Twaalf landen waaronder Nederland, hebben de oprichting mogelijk gemaakt. In de discussies is even sprake van vestiging in Nederland. Het wordt uiteindelijk Genève, Zwitserland.
Signing in Amsterdam of the treaty establishing CERN, a particle physics laboratory. Twelve countries, including the Netherlands, made its establishment possible. During the discussions, there was some talk of locating it in the Netherlands. Ultimately, it was decided to establish it in Geneva, Switzerland.
Oprichting van de landelijke werkgroep mesonenfysica, ter voorbereiding van toekomstige experimenten op het nieuwe CERN. Bij de universiteiten in Amsterdam, Nijmegen en Utrecht ontstaan activiteiten in de deeltjesfysica.
Establishment of the national meson physics working group, in preparation for future experiments at the new CERN. Activities in particle physics are emerging at the universities in Amsterdam, Nijmegen and Utrecht.
Een groep bij de Universiteit Utrecht bouwt het eerste Nederlandse pionen-experiment bij het SC synchrocyclotron in Genève, dat tot 1960 blijft bestaan. De SC is de eerste versneller bij CERN die bundels voor onderzoek produceert.
A group at Utrecht University builds the first Dutch pion experiment at the SC synchrocyclotron in Geneva, which remains in operation until 1960. The SC is the first accelerator at CERN to produce beams for research purposes.
Opening op CERN van het protosynchrotron PS en de opkomst van het bellenvat waarvan de beelden van deeltjessporen meer en meer automatisch worden gescand en opgemeten. Op het Mathematisch Centrum Amsterdam (nu CWI) komt de X1 computer in gebruik voor analyses en berekeningen, dan nog in ALGOL60 geprogrammeerd.
Opening of the PS protosynchrotron at CERN and the emergence of the bubble chamber, which increasingly scans and measures particle tracks automatically. At the Amsterdam Mathematical Centre (now CWI), the X1 computer is put into use for analyses and calculations, still programmed in ALGOL60.
Werkgroep Hoge-Energiefysica splitst zich af van de bestaande Werkgemeenschap Kernfysica. Doel is het bouwen en gebruiken van deeltjesversnellers, analyses van metingen en theoretisch werk. Vanaf 1964 werken Nederlandse deeltjesfysici als bezoekers op CERN. De universiteit Nijmegen begint een afdeling hoge-energiefysica, vanaf 1967 aangevuld met FOM-technici.
The High Energy Physics Working Group splits off from the existing Nuclear Physics Working Group. Its aim is to build and use particle accelerators, analyse measurements and carry out theoretical work. From 1964 onwards, Dutch particle physicists work as visitors at CERN. The University of Nijmegen starts a high-energy physics department, which is supplemented by FOM technicians from 1967 onwards.
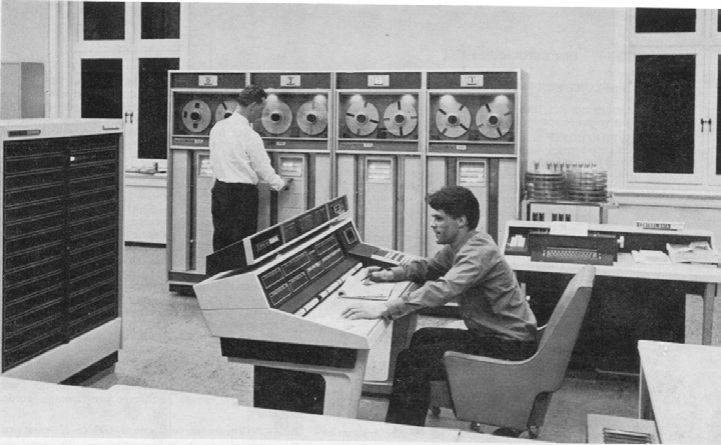
Eerste eigen computer voor deeltjesfysici in het Zeeman-lab in Amsterdam. De eerste dradenkamers voor detectoren op CERN worden gebouwd in de voormalige SONCO-textielfabriek tegenover het Zeeman-laboratorium.
First computer for particle physicists at the Zeeman Laboratory in Amsterdam. The first wire chambers for detectors at CERN are built in the former SONCO textile factory opposite the Zeeman Laboratory.
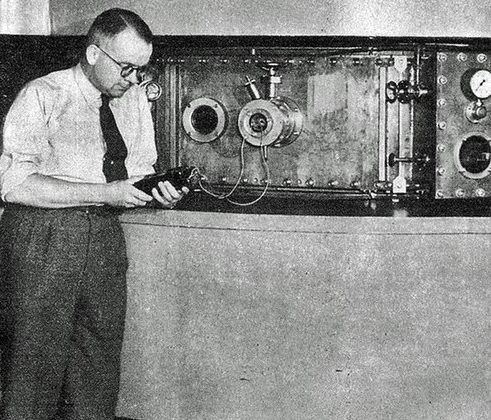
Bouw van de lineaire elektronenversneller EVA bij IKO in Amsterdam met uiteindelijk 100 MeV bundelenergie. Nauwkeurige studies van elektrische en magnetische structuur van talloze atoomkernen. In bedrijf tot 1976.
Construction of the linear electron accelerator EVA at IKO in Amsterdam with ultimately 100 MeV beam energy. Precise studies of electrical and magnetic structure of numerous atomic nuclei. In operation until 1976.
CERN opent een ringvormige opslag voor deeltjes, de Intersecting Storage Rings (ISR). Nederland concentreert zich op experimenten bij de Proton Synchrotron (PS) en de Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) en bouwt mee aan de benodigde detectoren. Bij de universiteiten van Amsterdam en Nijmegen worden opnames van deeltjessporen automatisch gescand en gedigitaliseerd. Eerste stap op weg naar een landelijk samenwerkingsverband, waar dan al vijf jaar over gesproken wordt.
CERN opens a ring-shaped storage facility for particles, the Intersecting Storage Rings (ISR). The Netherlands focuses on experiments at the Proton Synchrotron (PS) and the Super Proton Synchrotron (SPS) and contributes to the construction of the necessary detectors. At the Universities of Amsterdam and Nijmegen, recordings of particle tracks are automatically scanned and digitised. This is the first step towards a national partnership, which has been under discussion for five years.
De Nederlandse regering formuleert een nationaal plan voor kern- en hoge-energiefysica, ook om de hoge kosten te spreiden van de nieuwe SPS-versneller op CERN en een lineaire elektronenversneller in Amsterdam.
The Dutch government is formulating a national plan for nuclear and high-energy physics, partly to spread the high costs of the new SPS accelerator at CERN and a linear electron accelerator in Amsterdam.
Onderzoek, ook door Nederlandse groepen, naar zogeheten neutrale stromen in grote bellenvaten als BEBC op CERN. Ondermeer bij de nieuwe SPS-versnellerring.
Research, including by Dutch groups, into so-called neutral currents in large bubble chambers such as BEBC at CERN. Among other places, at the new SPS accelerator ring.
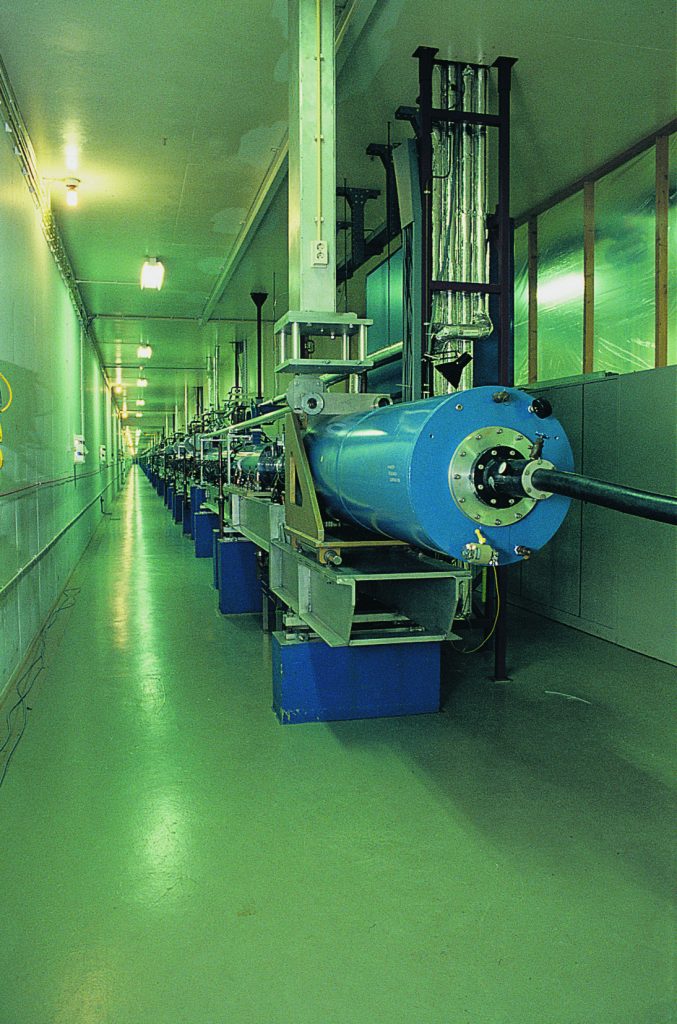
Bouw van de 200 meter lange MEA-elektronenversneller in een lange betonnen tunnel langs de Ringdijk in Amsterdam. Vanaf 1981 experimenten met spectrometers en dradenkamers. Internationaal toonaangevende studies van de bewegingen van protonen in atoomkernen met 500 MeV-elektronen. In gebruik tot 1998. Modulatorhal later gebruikt als internationaal hoofdknooppunt voor het internet.
Construction of the 200-metre-long MEA electron accelerator in a long concrete tunnel along the Ringdijk in Amsterdam. From 1981, experiments with spectrometers and wire chambers. Internationally leading studies of proton movements in atomic nuclei with 500 MeV electrons. In use until 1998. Modulator hall later used as international main hub for the internet.
Na moeizame onderhandelingen over vestiging, zeggenschap en werkverdeling wordt op 17 juni 1975 het Nationaal Instituut voor Kernfysica en Hoge-EnergieFysica (NIKHEF, later werd dit Nikhef) opgericht. Er komt een nieuw hoofdgebouw in Amsterdam. Ondertekenaars van de overeenkomst zijn FOM, kernonderzoeksinstituut IKO, de Universiteit van Amsterdam en de Katholieke Universiteit Nijmegen. Er komen twee secties, ieder met een eigen directeur: K voor kernfysica, en H voor hoge-energiefysica.
After difficult negotiations on location, control and division of labour, the National Institute for Nuclear physics and High-Energy Physics (NIKHEF, later to become Nikhef) was founded on 17 June 1975. A new main building will be built in Amsterdam. Signatories to the agreement are FOM, nuclear research institute IKO, the University of Amsterdam and Catholic University Nijmegen. There will be two sections, each with its own director: K for Kernfysica (nuclear physics), and H for high-energy physics.
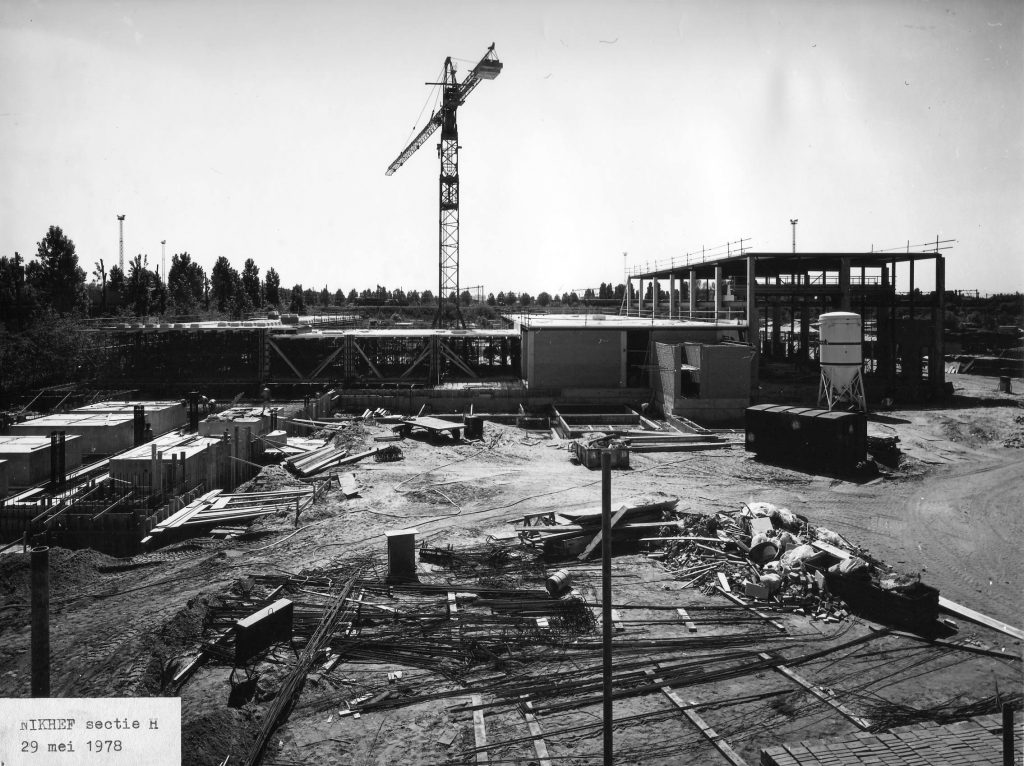
Bouw begint van het eigen Nikhef-gebouw in de Watergraafsmeer tussen IKO en AMOLF. De ruime assemblagehal van de mechanische werkplaats wordt als eerste opgeleverd.
Construction begins on Nikhef’s own building in Watergraafsmeer, between IKO and AMOLF. The spacious assembly hall of the mechanical workshop will be the first to be completed.
Nikhef raakt betrokken bij de jacht op W- en Z-deeltjes op CERN, in het UA1-experiment in de SPS-versneller. Nederland bouwt ook componenten voor andere experimenten, zoals dradenkamers voor het verderop gelegen UA4. W en Z worden in 1983 gevonden. Simon van der Meer en Carlo Rubbia ontvangen er de Nobelprijs voor de Natuurkunde voor in 1984.
Nikhef becomes involved in the search for W and Z particles at CERN, in the UA1 experiment in the SPS accelerator. The Netherlands also builds components for other experiments, such as wire chambers for the UA4 experiment further down the line. W and Z are discovered in 1983. Simon van der Meer and Carlo Rubbia receive the Nobel Prize in Physics for this discovery in 1984.
Eerste experimenten met silicium-detectoren voor deeltjesfysica, samen met ondermeer München, veel preciezer dan andere detectiemethodes. Opkomst van de elektronische expertise bij Nikhef.
First experiments with silicon detectors for particle physics, together with Munich, among others, much more precise than other detection methods. Emergence of electronic expertise at Nikhef.
De Amsterdamse H-sectie verhuist in juni 1980 van het Zeeman-lab naar de nieuwbouw. Op de eerste verdieping wordt de computerzaal ingericht. Ook de Universiteit Utrecht en de Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam sluiten zich aan bij Nikhef.
In June 1980, the Amsterdam Nikhef-H section moved from the Zeeman lab to the new building. The computer room was set up on the first floor. Utrecht University and VU University Amsterdam also joined Nikhef.
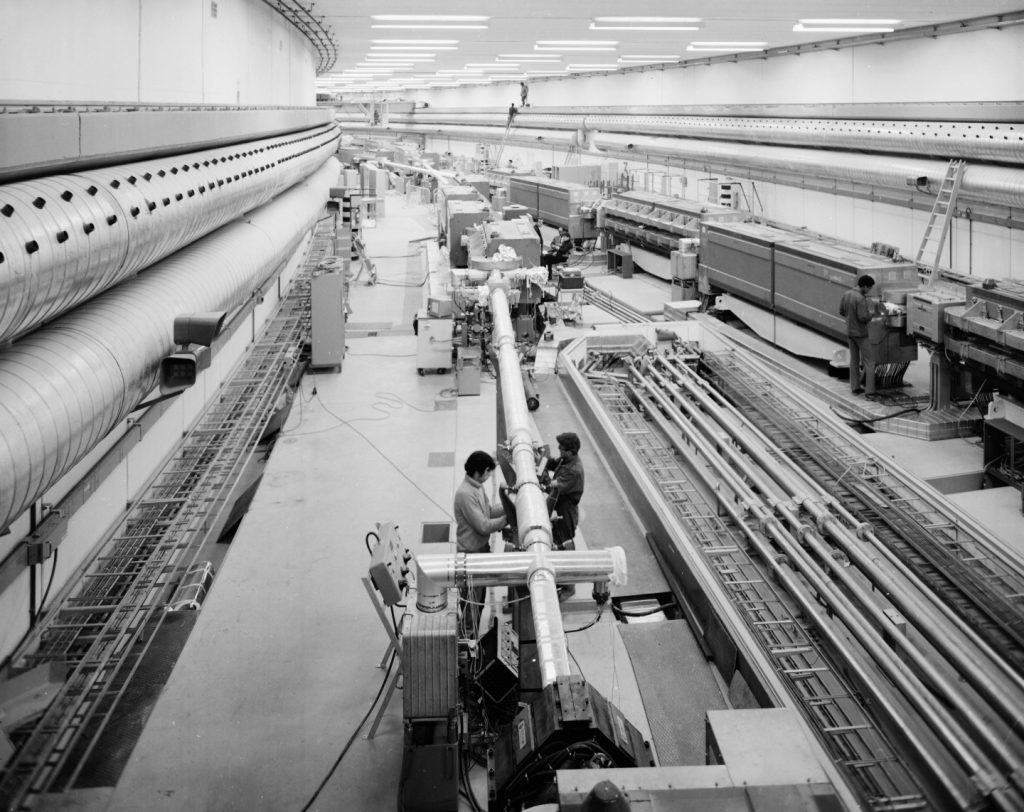
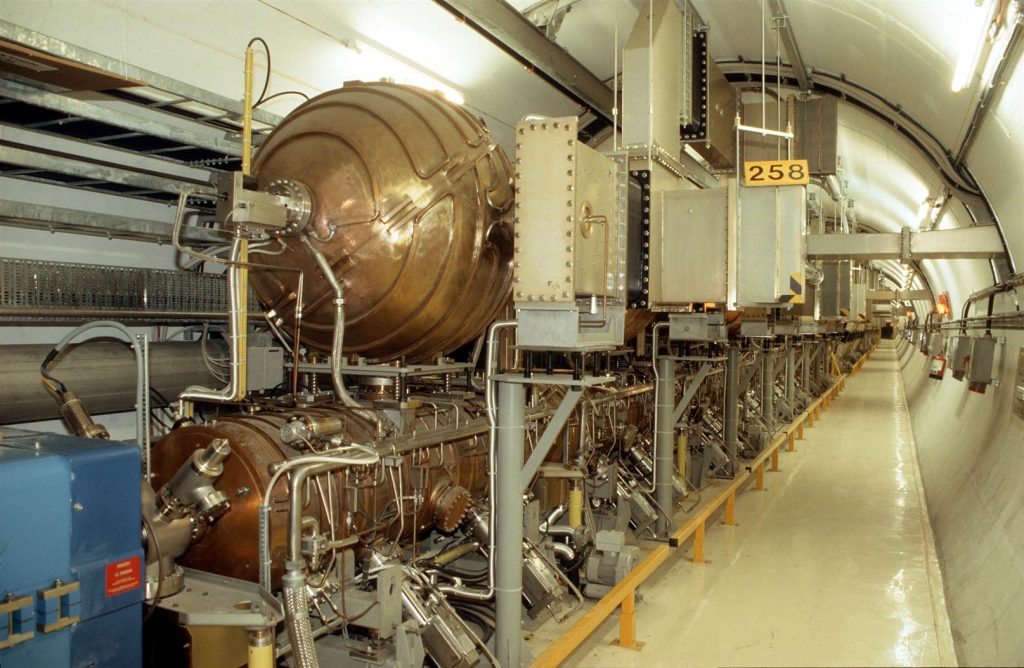
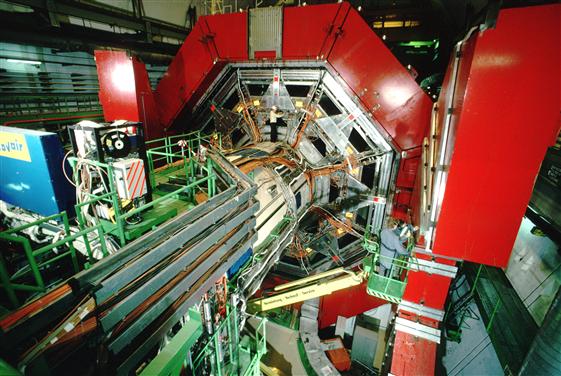
CERN besluit tot de bouw van Large Electron Positron versneller. Deze LEP wordt de grootste en krachtigste versneller ter wereld met een omtrek van 27 kilometer, 100 meter onder de grond. Nikhef kan dankzij de grote werkplaats aan zeker twee van de voorgestelde vier experimenten meebouwen; ondermeer muonkamers en draagconstructies voor detectoren.
CERN decides to build the Large Electron Positron accelerator. This LEP will be the largest and most powerful accelerator in the world, with a circumference of 27 kilometres, 100 metres below ground. Thanks to its large workshop, Nikhef will be able to contribute to at least two of the four proposed experiments, including muon chambers and support structures for detectors.
Start PIMU-experiment aan het uiteinde van de MEA-versneller. Bundels pionen en muonen voor de kernvangst en verstrooiingsexperimenten. Hal wordt later hergebruikt als constructiewerkplaats voor KM3NeT-modules.
Start PIMU experiment at the end of the MEA accelerator. Bundles of pions and muons for core capture and scattering experiments. Hall later reused as construction workshop for KM3NeT modules.
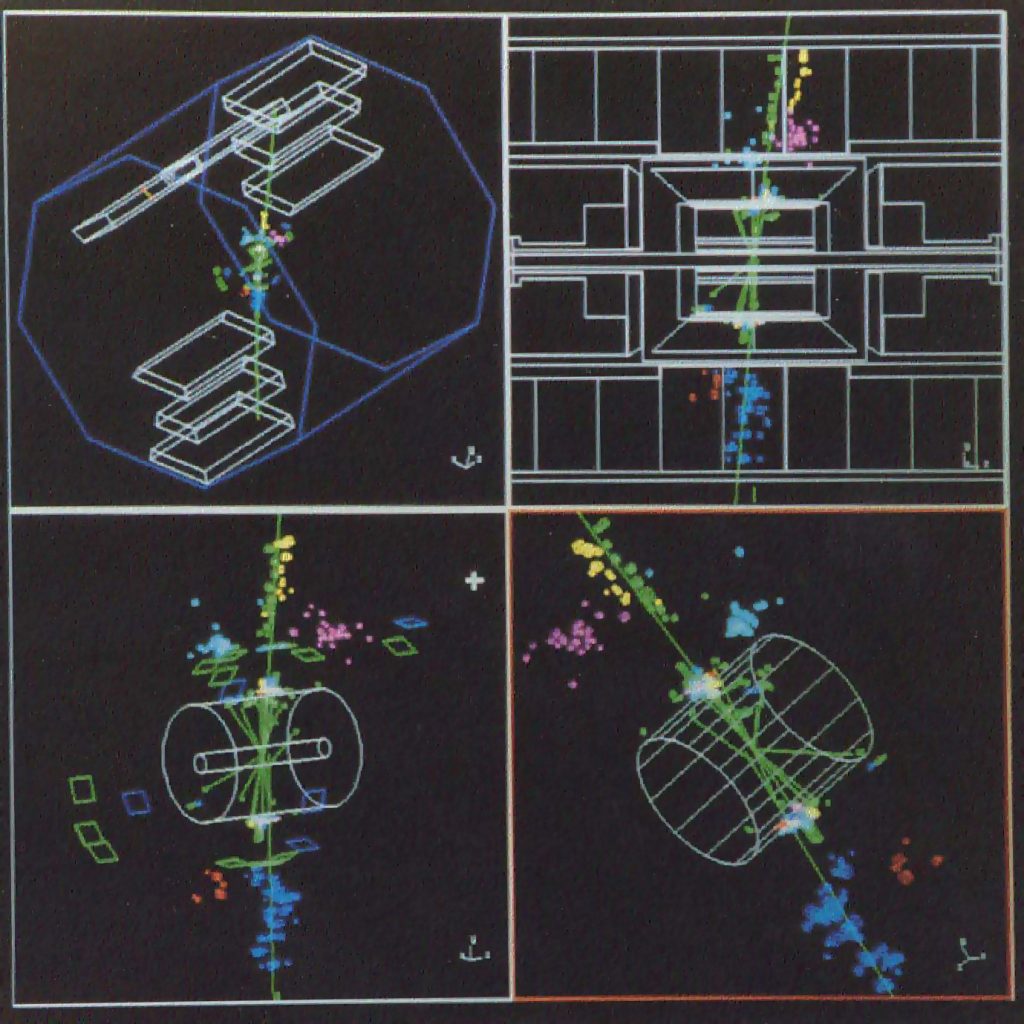
Ethernet computernetwerk in gebruik op het WCW (Stichting Wetenschappelijk Centrum Watergraafsmeer). Nikhef ontwikkelt veelgebruikte visualisatiesoftware voor deeltjesbotsingen.
Ethernet computer network in use at the WCW (Watergraafsmeer Scientific Centre Foundation). Nikhef develops widely used visualisation software for particle collisions.
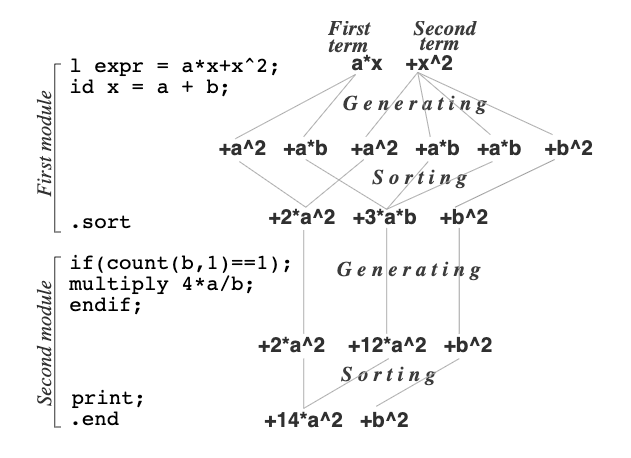
Theoretisch fysicus Jos Vermaseren van Nikhef introduceert het computeralgebraprogramma FORM voor nauwkeurige berekeningen in de deeltjesfysica. Het programma kan duizenden Feynmandiagrammen met miljoenen termen verwerken. FORM werd een van de standaardgereedschappen voor theoretici wereldwijd.
Theoretical physicist Jos Vermaseren of Nikhef introduces the computer program FORM for accurate calculations in particle physics. The program can handle thousands of Feynman diagrams with millions of terms. FORM became one of the standard tools for theorists worldwide.
LEP in gebruik. Legt kwantitatieve basis voor het Standaardmodel en geeft impuls aan Nobelprijs voor Veltman en ’t Hooft. LEP jaagt tot de sluiting in 2000 tevergeefs op het voorspelde higgsdeeltje waarvoor de versneller onvoldoende energie heeft. Nikhef was nauw betrokken bij twee experimenten: DELPHI en L3.
LEP in use. Provides quantitative basis to the Standard Model and leads to a Nobelprize for Veltman and ’t Hooft. Until its closure in 2000, LEP searched in vain for the predicted Higgs particle, for which the accelerator did not have sufficient energy. Nikhef was closely involved in two experiments: DELPHI and L3.
CERN maakt eerste plannen voor een nieuwe versneller, de Large Hadron Collider. De LHC is een proton-protonbotser met supergeleidende magneten, te bouwen in de bestaande LEP-tunnel van 27 kilometer omtrek. Plannen worden eind 1994 goedgekeurd.
CERN makes initial plans for a new accelerator, the Large Hadron Collider. The LHC is a proton-proton collider with superconducting magnets, to be built in the existing LEP tunnel with a circumference of 27 kilometres. Plans are approved at the end of 1994.
Uitbreiding van de MEA-versneller in Amsterdam met 212 meter lange pulsstretcher-ring, die elektronenpulsen uitsmeert waardoor zeldzamer processen zichtbaar worden. AmPS wordt ook gebruikt als opslagring. Later nog aangevuld met de “siberische slang” om gepolariseerde bundels te maken voor studies van asymmetrische kernprocessen. Eind 1998 gesloten en ontmanteld. Hallen worden rond 2018 afgebroken.
Extension of the MEA accelerator in Amsterdam with 212-metre-long pulse-stretcher ring, which smears electron pulses, making rarer processes visible. AmPS is also used as a storage ring. Later supplemented by the “siberian snake” to create polarised beams for studies of asymmetric nuclear processes. Closed and dismantled at the end of 1998. Halls were demolished around 2018.
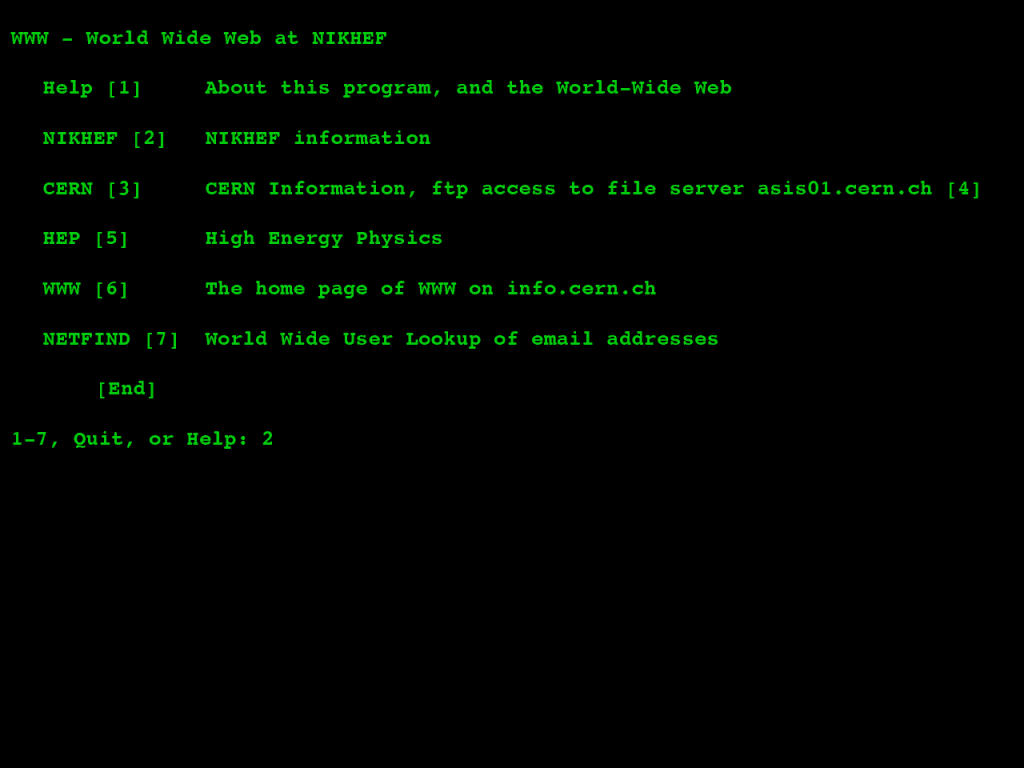
Nikhef.nl wordt eerste website in Nederland, een van de eerste drie webpagina’s in de wereld.
Lees meer over Nikhef en het WWW
Nikhef.nl becomes the first website in the Netherlands, one of the first three web pages in the world.
Read more about Nikhef and the WWW
Sluiting MEA-elektronenversneller, afdeling Kernfysica wordt opgeheven. De naam van het instituut verandert in Nationaal instituut voor subatomaire fysica. Focus ligt op hoge-energiefysica. Leden van de K-sectie nog wel betrokken bij experimenten in Duitsland (DESY HERMES), Zweden en de VS. Nikhef is in het vervolg geen afkorting meer, maar een eigennaam.
Electron accelerator MEA closed, Department of Nuclear Physics disbanded. Institute name changes to National Institute of Subatomic Physics. Focus is on high-energy physics. Members of the K-section still associated with other experiments in Germany (DESY HERMES), Sweden and the US. Nikhef is henceforth no longer an abbreviation, but a proper name.
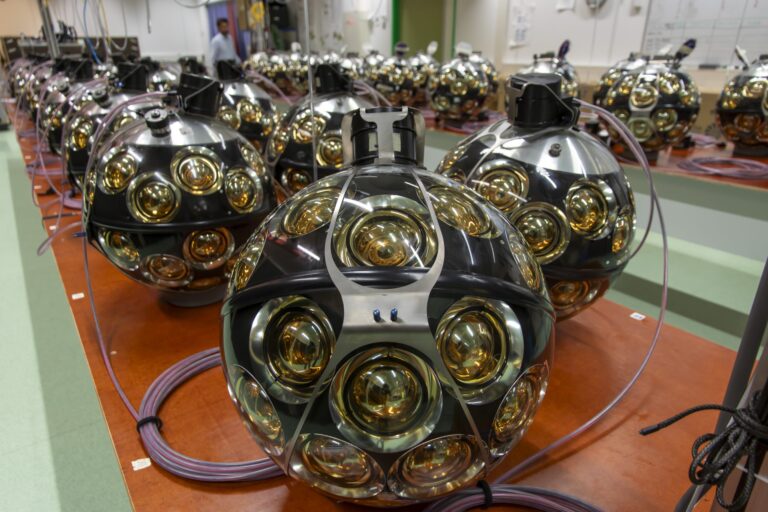
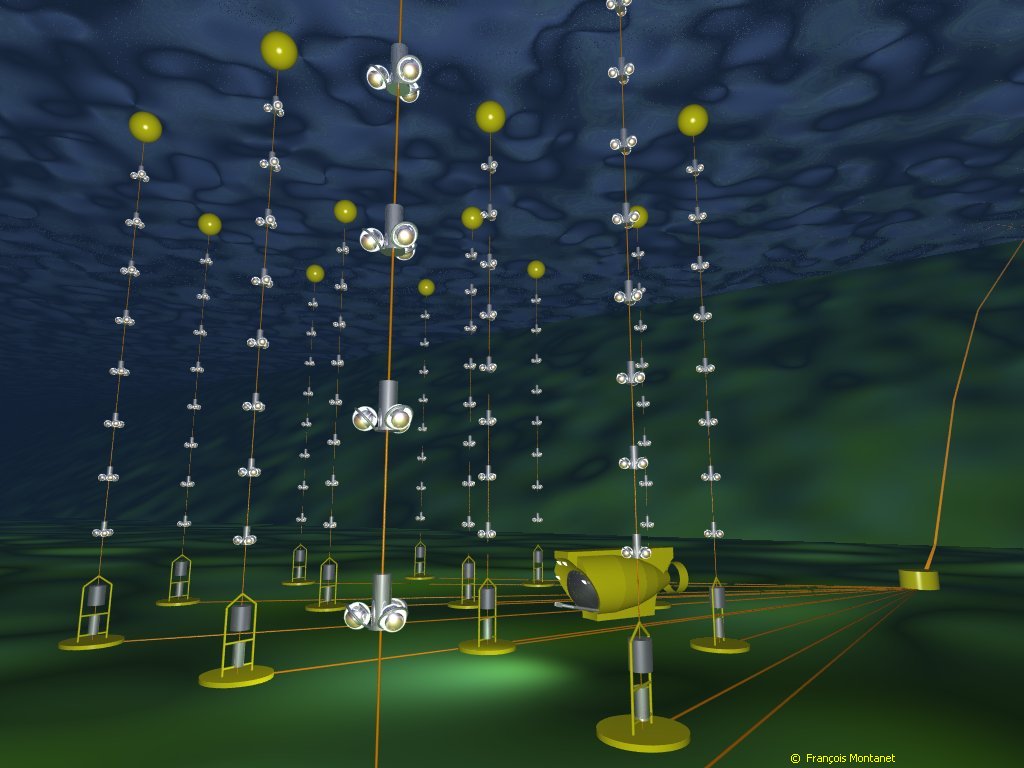
Nikhef verbreedt onderzoeksagenda met astrodeeltjesfysica, plan voor de neutrinotelescoop ANTARES in de Middellandse zee; dat is de voorloper van de huidige onderzeese neutrinotelescoop KM3NeT, waarvoor grote delen in Amsterdam worden ontworpen en gebouwd. Wat later volgt via Nikhef / Radboud Universiteit Nijmegen ook het Auger-observatorium voor kosmische straling in Argentinië.
Nikhef broadens its research agenda with astroparticle physics, plans for the ANTARES neutrino telescope in the Mediterranean Sea; this is the precursor to the current KM3NeT underwater neutrino telescope, large parts of which are being designed and built in Amsterdam. A little later, Nikhef / Radboud University Nijmegen will also be involved in the Auger observatory for cosmic radiation in Argentina.
Eerste aanwijzingen voor quark-gluonplasma in experimenten met goud en loodionen op CERN, mede door Nederlandse fysici uitgevoerd. LEP-versneller op CERN sluit en wordt in 2001 ontmanteld.
First indications of quark-gluon plasma in experiments with gold and lead ions at CERN, partly carried out by Dutch physicists. LEP accelerator at CERN closes and is dismantled in 2001.
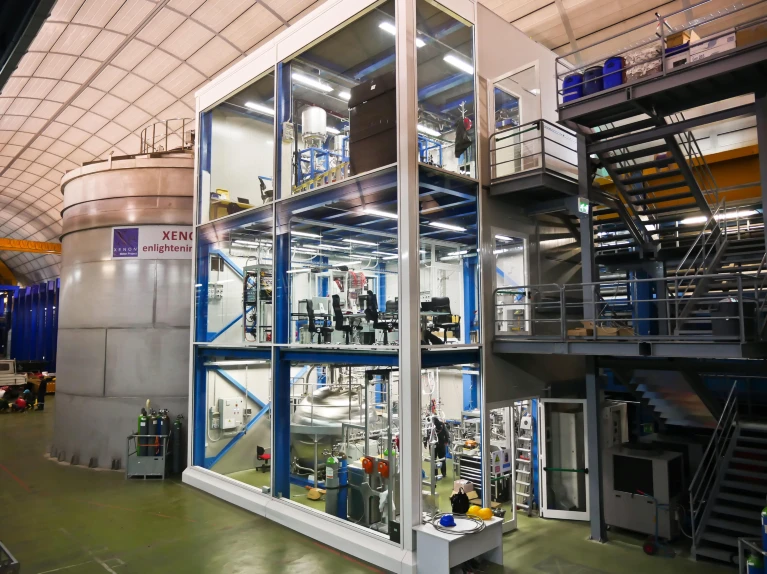
Verdere verbreding Nikhef-agenda met onderzoek naar donkere materie, door deelname aan XENON-experiment op Gran Sasso, Italië. Centrale rol Nikhef-technici bij verdere upgrades.
Further expansion of Nikhef’s agenda with research into dark matter, through participation in the XENON experiment at Gran Sasso, Italy. Central role for Nikhef technicians in further upgrades.
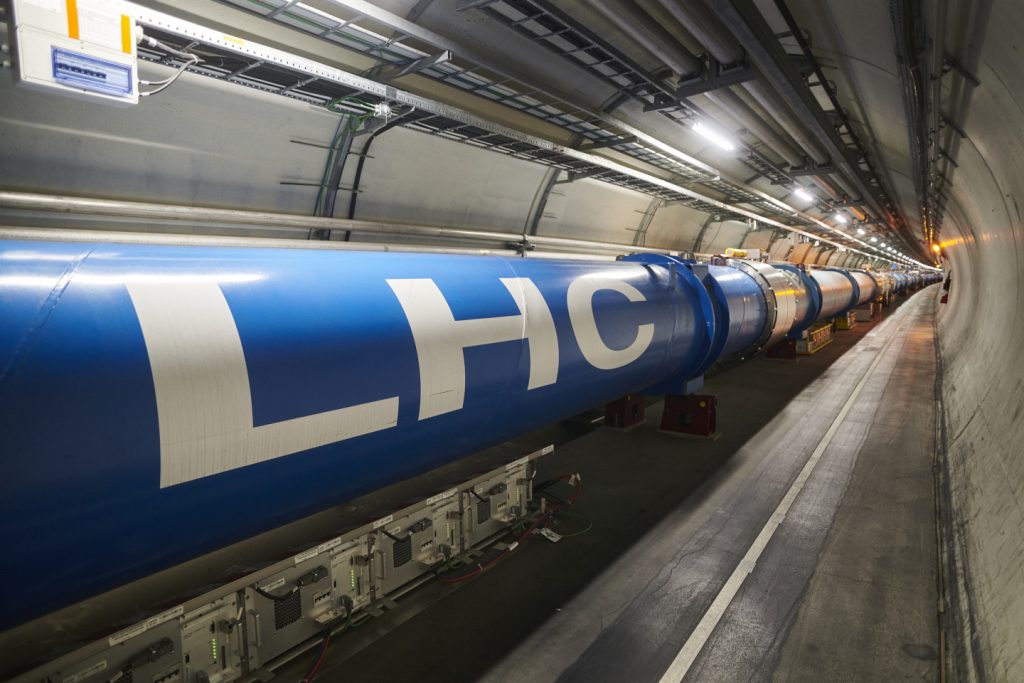
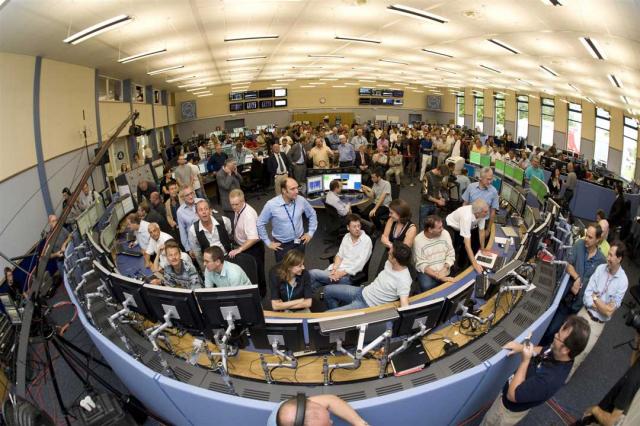
Start van de Large Hadron Collider. Nederland is via Nikhef betrokken bij het ontwerp en de bouw van drie van de vier grote experimenten: ALICE, ATLAS en LHCb. Na startproblemen zijn de eerste protonenbundels in de LHC in 2010 een feit.
Start of the Large Hadron Collider. Through Nikhef, The Netherlands is involved in the design and construction of three of the four major experiments: ALICE, ATLAS and LHCb. After initial problems, the first proton beams in the LHC became a reality in 2010.
Ontdekking van het higgsdeeltje op CERN met de LHC-versneller. Nederland is via Nikhef nauw betrokken bij de jarenlange metingen en analyses van de data. De bekendmaking trekt ook in Amsterdam grote belangstelling van de media.
Discovery of the Higgs particle at CERN using the LHC accelerator. Through Nikhef, The Netherlands is closely involved in the years of measurements and analyses of the data. The announcement also attracts considerable media interest in Amsterdam.
Ontdekking van zwaartekrachtsgolven met LIGO- en Virgo-detectoren in de VS en Italië. De al door Einstein voorspelde rillingen van ruimte en tijd worden veroorzaakt door botsende zwarte gaten. Nikhef is een van de partners in het internationale onderzoek. In 2017 kondigen de onderzoekers aan zwaartekrachtsgolven te hebben ontdekt van twee neutronensterren.
Discovery of gravitational waves with LIGO and Virgo detectors in the US and Italy. The ripples in space and time predicted by Einstein are caused by colliding black holes. Nikhef is one of the partners in the international research. In 2017, researchers announced that they had discovered gravitational waves from two neutron stars.
Rijksuniversiteit Groningen treedt toe tot de Nikhef-samenwerking. Het Van Swinderen Instituut doet onder meer onderzoek naar de fundamentele eigenschappen van het elektron.
The University of Groningen joins the Nikhef partnership. The Van Swinderen Institute conducts research into the fundamental properties of the electron, among other things.
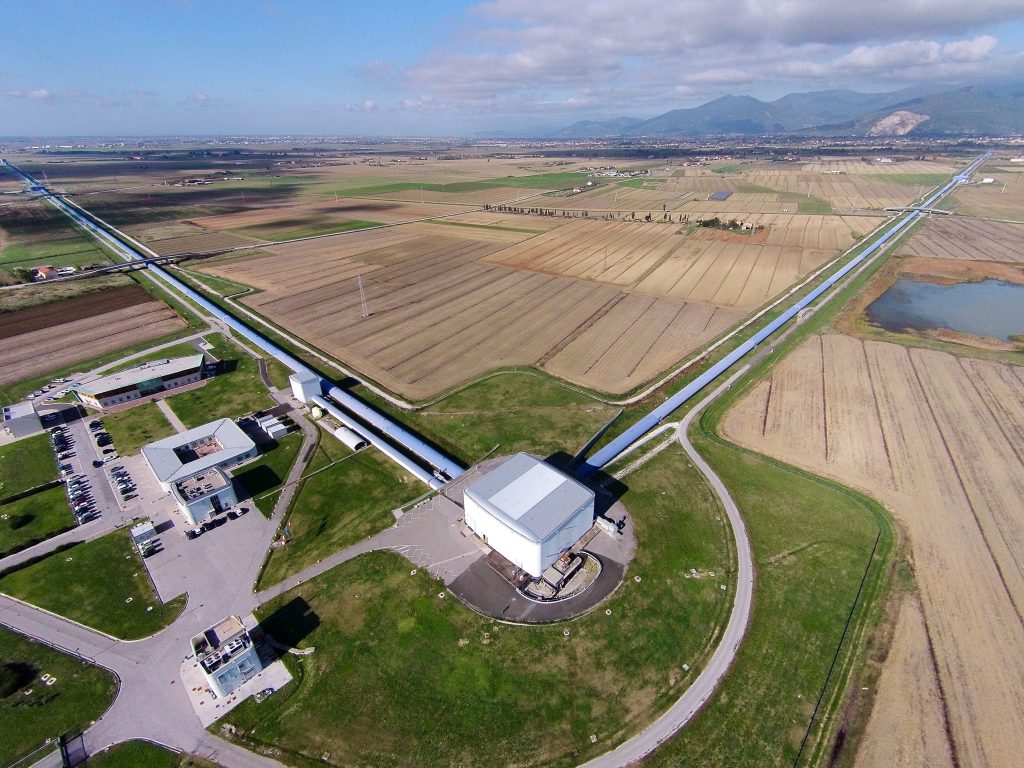
Universiteit Maastricht treedt toe tot de Nikhef-samenwerking. De fysica-afdeling doet onderzoek in de deeltjesfysica en is nauw betrokken bij plannen voor de Einstein Telescoop voor zwaartekrachtsgolven, mogelijk in Limburg. Ook wordt in Maastricht de ETpathfinder testfaciliteit gebouwd.
Maastricht University joins the Nikhef partnership. The physics department conducts research in particle physics and is closely involved in plans for the Einstein Telescope for gravitational waves, possibly in Limburg. The ETpathfinder test facility is also being built in Maastricht.
Renovatie van het Nikhef-gebouw op Amsterdam Science Park officieel van start. De renovatie is eind 2023 voltooid en op 29 februari 2024 wordt het gebouw feestelijk heropend.
Renovation of the Nikhef building at Amsterdam Science Park officially underway. The renovation will be completed by the end of 2023, and the building will be festively reopened on 29 February 2024.
Waarneming van het meest energetische neutrino ooit met de KM3NeT-detector in de Middellandse Zee, met een grote inbreng van Nikhef, waar grote delen van de detector worden gebouwd en data geanalyseerd. Het record haalt de cover van het tijdschrift Nature.
Observation of the most energetic neutrino ever detected with the KM3NeT detector in the Mediterranean Sea, with a major contribution from Nikhef, where large parts of the detector are being built and data analysed. The record makes the cover of Nature magazine.
Op 17 juni 2025 vierde het Nikhef-samenwerkingsverband zijn 50e verjaardag. Er kan worden uitgekeken naar vele meer decennia baanbrekend onderzoek.
On 17 June 2025, the Nikhef partnership celebrated its 50th anniversary. We can look forward to many more decades of groundbreaking research.