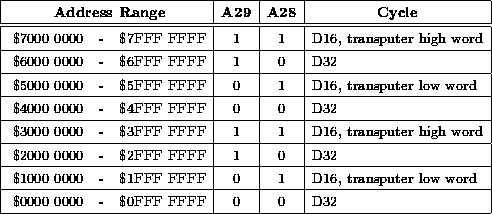
Table 2: Longword/word selection by address bits A29 and A28.
In the address ranges $C000 0000 - $FFFF FFFF and $8000 0000 - $BFFF FFFF 'normal' 32-bits transputer read/write cycles are mapped onto two D16 VME-cycles (first a cycle to write the high order word of the transputer longword, then a cycle to write the low order word of the transputer longword). 'Normal' is when the lock flag in Statusregister 2 is NOT set (see section 4 on the Statusregisters). When the lock flag is set a D8 cycle is performed (see section 3.6 on D8 cycles).
In the address ranges $4000 0000 - $7FFF FFFF and $0000 0000 - $3FFF FFFF 32-bits transputer read/write cycles are mapped onto a single VME D16 cycle if address bit A28 is set, where the word within the longword read or written is selected by address bit A29 :

Table 2: Longword/word selection by address bits A29 and A28.
Example: if a word value is to be read from VME-address
$A000 1000 by
an A32 D16 VME-cycle in OCCAM it can be done as follows :
[4]INT statusregister :
PLACE statusregister AT ((#82000000 >< MOSTNEG INT) >> 2) :
[2]INT16 words :
-- To access word 0 in VME access word 1 on the transputer
-- so place 'longword' at word 1 (transputer high word) memory
-- segment in A32 area
PLACE words AT ((#70001000 >< MOSTNEG INT) >> 2) :
word.address.1000 IS words[1] :
INT16 value :
SEQ
statusregister[2] := #0F -- Reset A31 to A28
statusregister[3] := #0A -- Set A31 to A28 to hex 'A'
value := word.address.1000 -- Read the word
or as follows if a longword value is to be read by an A32 D16 VME-cycle:
[4]INT statusregister :
PLACE statusregister AT ((#82000000 >< MOSTNEG INT) >> 2) :
INT longword :
-- To access word 0 in VME access word 1 on the transputer
-- so place 'longword' at word 1 (transputer high word) memory
-- segment in A32 area
PLACE longword AT ((#70001000 >< MOSTNEG INT) >> 2) :
INT value :
SEQ
statusregister[2] := #0F -- Reset A31 to A28
statusregister[3] := #0A -- Set A31 to A28 to hex 'A'
-- Read the word and shift it to the low word
value := (longword /\ #FFFF0000) >> 16